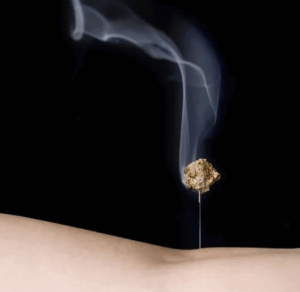
What Is Moxibustion or Moxa?
Moxibustion, often called “moxa,” is a traditional therapeutic practice that involves burning small cones of dried and aged herb known as moxa near or on specific acupuncture points on the body. The term “moxa” is derived from the Japanese word “mogusa” (もぐさ), meaning “burning herb.” This practice is divided into indirect moxibustion, where the burning moxa is held close to the skin, and direct moxibustion, placed directly on the skin. Direct moxibustion uses tiny amounts of moxa that create a pleasant warmth on the skin. When done correctly by a trained practitioner, it should feel soothing and never cause burns or discomfort.
Moxa, also known as mugwort or Artemisia vulgaris, is an herb revered in traditional medicine. Its preparation involves harvesting mugwort leaves, drying them, and then finely grinding them into a fluffy, wool-like texture. The quality of moxa is determined by the ratio of leaves to trichomes (fine, soft hairs found on the back of the leaves). Gold moxa considered the highest quality, features a 1:30 ratio of leaves to trichomes.
The earliest recorded mention of moxibustion is found in the “Huangdi Neijing,” a Chinese medical text compiled around the 2nd century BCE. This text documents the various forms of moxibustion and their applications in treating ailments. Moxibustion was introduced to Japan during the Nara period (710-794 CE) alongside the spread of Buddhism. The integration of moxibustion into Japanese culture led to the development of unique techniques and styles that continue to be practiced today.
In my practice, I emphasise on moxibustion, giving it the same attention as acupuncture. While I utilise Chinese moxibustion techniques, I also specialise in Fukayakyo (深谷灸法), a specific style of Japanese moxibustion developed by the renowned scholar Isaburo Fukaya Sensei (1900-1974). Fukayakyo moxibustion is characterised by its gentle and sustained application of high-quality moxa (gold grade) to specific acupuncture points or areas of the body. This technique employs a bamboo tube and a slow-burning approach, producing a profoundly penetrating and warming effect that enhances the therapeutic benefits of treatment.
get in touch
Have any questions about Acupuncture and Moxibustion treatments? Sara is available to discuss your health concerns and treatment options.
Copyright © 2023- 2026 Acupuncture Moxa Melbourne – All Rights Reserved.
